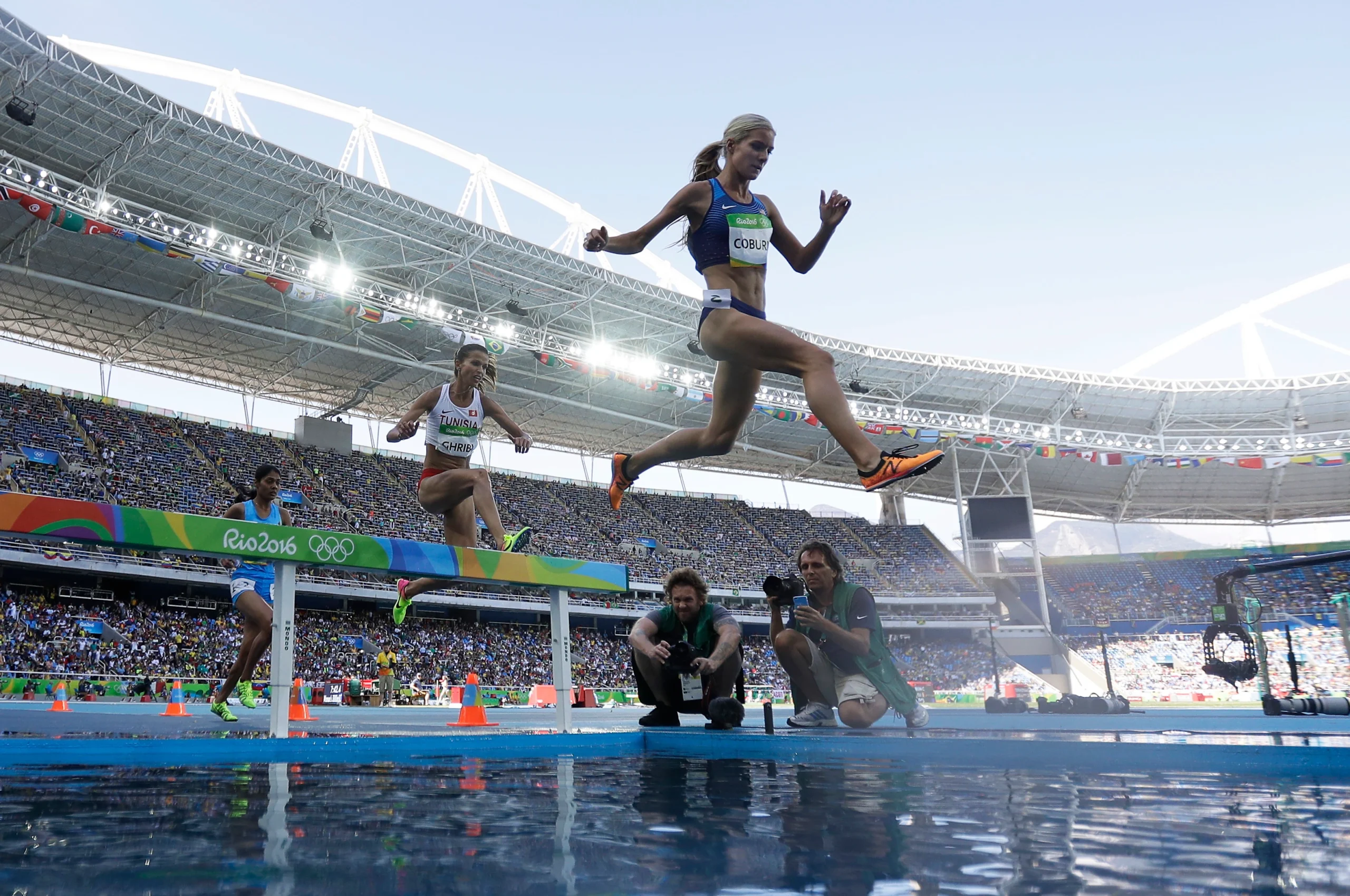
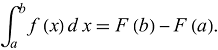The steeplechase event requires a combination of speed, endurance, and jumping ability, as athletes must clear the barriers while maintaining their pace and negotiating the water jump. The rules and specifications for the steeplechase event are set by the International Association of Athletics Federations the governing body for the sport of athletics (track and field) worldwide; with minor adaptations by the NCAA for intercollegiate competition.
The steeplechase is a distance race with barriers and a water pit that athletes must clear during the race. According to the NCAA Track and Field and Cross Country rulebook, the standards for the steeplechase water jump are as follows:
- Length: The water pit must be at least 3.66 meters (12 feet) long.
- Width: The water pit must be at least 3.66 meters (12 feet) wide.
- Depth: The water pit must have a minimum depth of 0.7 meters (2 feet 4 inches) and a maximum depth of 0.9 meters (2 feet 11 inches).
- Slope: The slope of the water pit must not exceed 1:5, meaning that for every 5 meters in length, the water pit can rise by no more than 1 meter in height.
- Barrier: The water pit must be preceded by a solid barrier that is 91.4 cm (3 feet) high. Athletes are required to clear this barrier before landing in the water pit.
These standards may be subject to change and may vary depending on the specific NCAA division (Division I, Division II, or Division III) and other factors such as venue requirements. Therefore, it’s always best to refer to the official NCAA rules and regulations for the most up-to-date and accurate information on the steeplechase water jump standards in NCAA competitions.
ASTM F 2157-09 (2018) Standard Specification for Synthetic Surfaced Running Tracks
This specification establishes the minimum performance requirements and classification when tested in accordance with the procedures outlined within this specification. All documents referencing this specification must include classification required.
ASTM F 2569-11 Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Force Reduction Properties of Surfaces for Athletic Use
This test method covers the quantitative measurement and normalization of impact forces generated through a mechanical impact test on an athletic surface. The impact forces simulated in this test method are intended to represent those produced by lower extremities of an athlete during landing events on sport or athletic surfaces.
ASTM F 2949-12 Standard Specification for Pole Vault Box Collars
This specification covers minimum requirements of size, physical characteristics of materials, standard testing procedures, labeling and identification of pole vault box collars.
ASTM F 1162/F1162M-18 Standard Specification for Pole Vault Landing Systems
This specification covers minimum requirements of size, physical characteristics of materials, standard testing procedures, labeling and identification of pole vault landing systems.
ASTM F 2270-12 (2018) Standard Guide for Construction and Maintenance of Warning Track Areas on Sports Fields
This guide covers techniques that are appropriate for the construction and maintenance of warning track areas on sports fields. This guide provides guidance for the selection of materials, such as soil and sand for use in constructing or reconditioning warning track areas and for selection of management practices that will maintain a safe and functioning warning track.
ASTM F 2650-17e1 Standard Terminology Relating to Impact Testing of Sports Surfaces and Equipment
This terminology covers terms related to impact test methods and impact attenuation specifications of sports equipment and surfaces.