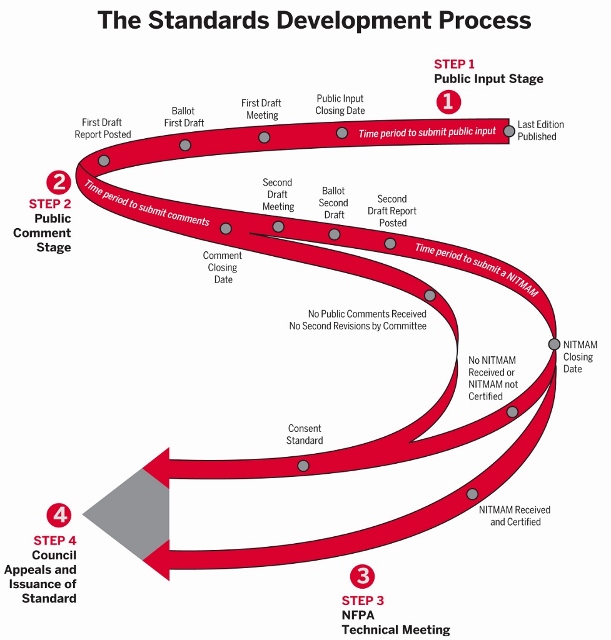
Much of our assertion that building construction in education communities resembles a perpetual motion machine rests upon innovation in a broad span of technologies that is effectively weather resistant; that along with development of construction scheduling. Today at 16:0 UTC we review the technical, management and legal literature that supports safe and sustainable construction,
1. Cold-Weather Concrete Technology
-
- Accelerating Admixtures: These are chemical additives that speed up the curing process of concrete, allowing it to set even in low temperatures.
- Heated Concrete Blankets: Electric blankets that maintain a consistent temperature around freshly poured concrete.
- Hot Water Mixing: Using heated water during the mixing process to ensure that concrete maintains the proper temperature for curing.
- Air-Entrained Concrete: Helps resist freeze-thaw cycles by creating tiny air pockets in the concrete.
2. Temporary Heating Solutions
-
- Portable Heaters: Diesel, propane, or electric heaters used to maintain a warm environment for workers and materials.
- Enclosed Workspaces: Temporary enclosures (tents or tarps) around construction areas retain heat and shield against snow and wind.
3. Advanced Building Materials
-
- Cold-Weather Asphalt: Modified asphalt that can be laid at lower temperatures.
- Pre-fabricated Components: Factory-assembled parts (walls, beams) that reduce on-site work in harsh conditions.
4. Insulation Techniques
-
- Insulated Tarps and Blankets: Used to cover construction materials and newly laid concrete to prevent freezing.
- Frost-Protected Shallow Foundations: Insulation techniques to keep ground temperatures stable and prevent frost heave.
5. Ground Thawing Technologies
-
- Hydronic Ground Heaters: Circulate heated fluid through hoses laid on frozen ground to thaw it before excavation or foundation work.
- Steam Thawing: Direct steam application to melt snow or thaw frozen soil.
6. Lighting Solutions
-
- High-Intensity LED Lights: Compensate for reduced daylight hours to ensure safe and efficient work conditions.
7. Weather-Resistant Machinery
-
- Winterized Equipment: Construction equipment with heated cabins, antifreeze systems, and enhanced traction for icy conditions.
8. Workforce Adaptations
-
- Cold-Weather Gear: Heated clothing, gloves, and footwear keep workers safe and productive.
- Modified Work Schedules: Shorter shifts or daytime-only work to limit exposure to extreme cold.
9. Snow and Ice Management
-
- Deicing Solutions: Chemical deicers and mechanical snow-removal equipment keep work areas safe and accessible.
- Heated Surfaces: Embedded heating systems in ramps or entryways prevent ice buildup.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration does not have a specific regulation solely dedicated to building construction in cold winter weather. However, several OSHA standards and guidelines are applicable to address the hazards and challenges of winter construction work. These regulations focus on worker safety, protection from cold stress, proper equipment use, and general site safety. Key applicable OSHA regulations and guidance include:
1. Cold Stress and Temperature Exposure
- General Duty Clause (Section 5(a)(1)): Employers are required to provide a workplace free from recognized hazards likely to cause death or serious physical harm. This includes addressing cold stress hazards, such as hypothermia, frostbite, and trench foot.
- OSHA Cold Stress Guide: OSHA provides guidance on recognizing, preventing, and managing cold stress but does not have a specific cold stress standard.
2. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
- 29 CFR 1926.28: Requires employers to ensure the use of appropriate personal protective equipment.
- 29 CFR 1910.132: General requirements for PPE, including insulated gloves, boots, and clothing to protect against cold weather.
3. Walking and Working Surfaces
- 29 CFR 1926.501: Fall Protection in Construction. Ice and snow can increase fall risks, so proper precautions, including removal of hazards and use of fall protection systems, are required.
- 29 CFR 1926.451: Scaffolding. Specific safety measures must be implemented to ensure stability and secure footing in icy conditions.
4. Snow and Ice Removal
- Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200): Ensures workers are informed about hazards related to de-icing chemicals or other substances used in winter construction.
5. Powered Equipment
- 29 CFR 1926.600: Equipment use, requiring machinery to be properly maintained and adjusted for cold-weather operations, including anti-freeze measures and winterization.
6. Excavations and Frost Heave
- 29 CFR 1926.651 and 1926.652: Excavation standards. Frozen ground and frost heave pose additional risks during trenching and excavation activities.
7. Temporary Heating
- 29 CFR 1926.154: Requirements for temporary heating devices, including ventilation and safe usage in confined or enclosed spaces.
8. Illumination
- 29 CFR 1926.56: Lighting standards to ensure sufficient visibility during reduced daylight hours in winter.
9. Emergency Preparedness
- First Aid (29 CFR 1926.50): Employers must ensure quick access to first aid, especially critical for treating cold-related illnesses or injuries.
10. Hazard Communication and Training
- 29 CFR 1926.21(b): Employers must train employees on recognizing winter hazards, such as slips, trips, falls, and cold stress.
By following these OSHA standards and implementing additional best practices (e.g., scheduling breaks in heated shelters, providing warm beverages, and encouraging layered clothing), employers can ensure a safer construction environment during winter conditions.
Related:
Electrical heat tracing: international harmonization-now and in the future