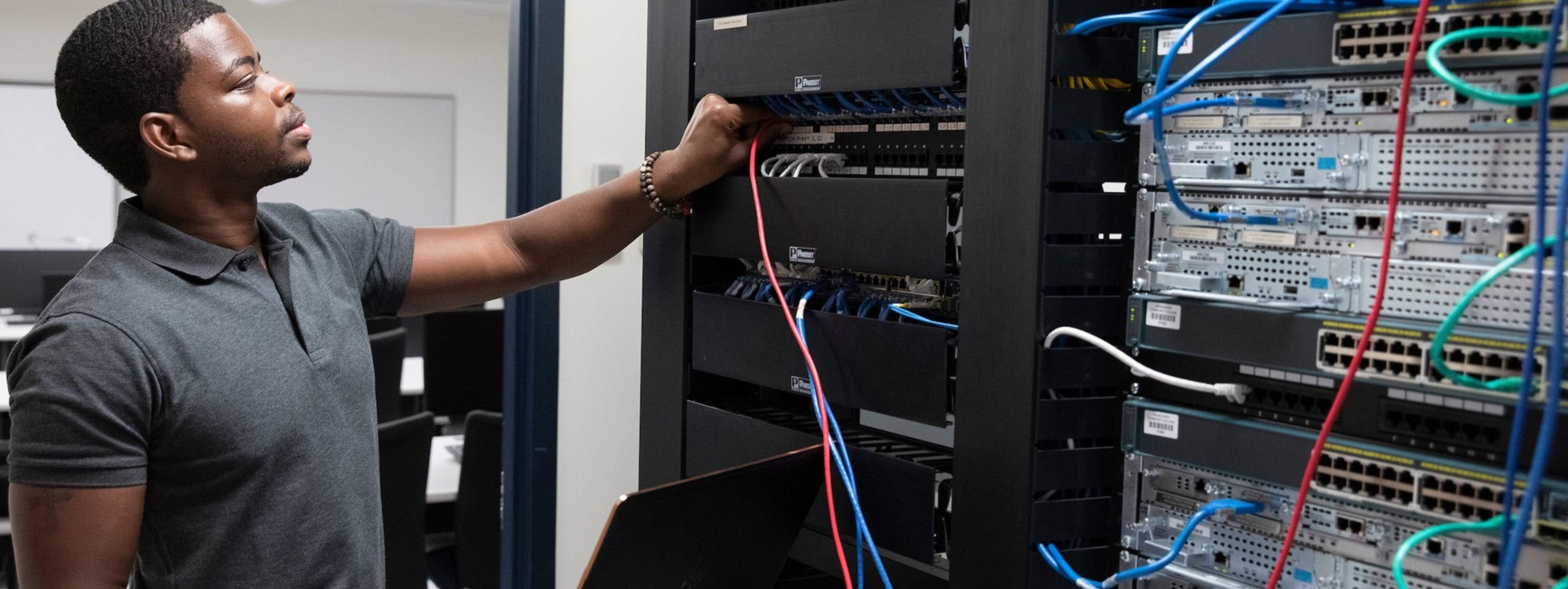
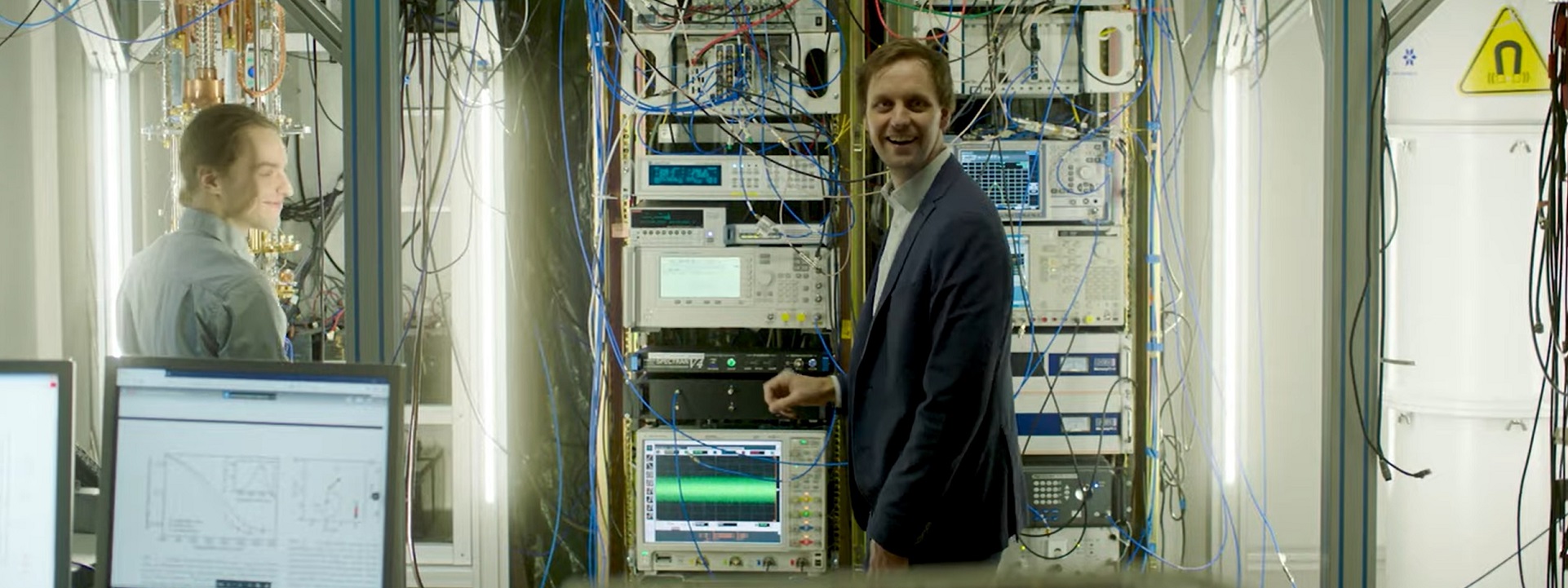
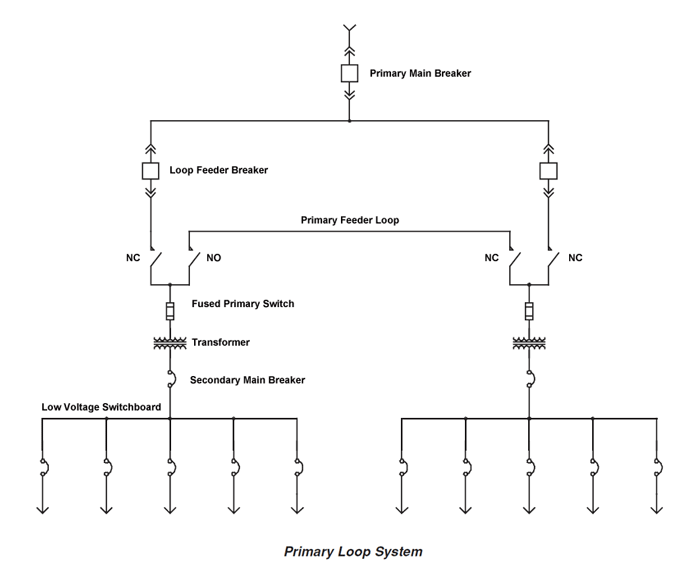
Today we get down in the weeds to examine the point of common coupling between a building and a telecommunication service provider. In many cases the TSP is the university itself.
TIA-758-C (2021) Customer-Owned Outside Plant Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard. Covers direct-buried cable, conduit systems, duct banks, handholes, manholes, burial depths, warning tape, backfill, and route planning. → Includes minimum bend radii, pulling tensions, separation from power, and environmental protection. Applies to copper, coaxial, and optical fiber in underground pathways.
TIA-590-B (2015) Standard for Physical Location and Protection of Below-Ground Fiber Optic Cable Plant. Focuses on fiber optic underground protection. → Specifies burial depths, marker tape, locator wires, armored vs. non-armored cable, and risk mitigation (e.g., flood zones).

Higher education settlements often require a more diverse approach to designing and implementing ICT systems than that of a typical commercial building. First of all, educational settlements are frequently one building. That means not only does the ICT infrastructure need to meet the varying demands of a specific building, but multiple buildings must all be integrated into one cohesive design.
In an environment of providing multifunctional spaces within one building, it is common to find a combination of commercial, industrial, data center, health care and entertainment environments within just a few buildings; hence our preference for the word “settlements” over the more widely used word “campus”.
TIA Standards
ANSI/TIA-568-C series: Telecommunications Cabling Standards. Specifies the requirements for various aspects of structured cabling systems, including cabling components, installation, and testing.
TIA-569-B: Telecommunications Pathways and Spaces. Provides guidelines for the design and installation of pathways and spaces for telecommunications cabling.
TIA-606-B: Administration Standard for Commercial Telecommunications Infrastructure. Specifies administration practices for the telecommunications infrastructure of commercial buildings.
Our inquiry cuts across the catalogs of several other standards developers:
NEC (National Electrical Code). NEC Article 800 specifically addresses the installation of communications circuits and equipment.
ISO/IEC 11801: Information technology — Generic cabling for customer premises. Defines generic telecommunications cabling systems (structured cabling) used for various services, including voice and data.
IEEE 802.3: Ethernet Standards. Defines standards for Ethernet networks, which are commonly used for data communication in buildings.
UL 497: Protectors for Paired Conductor Communications Circuits. Addresses requirements for protectors used to safeguard communications circuits from overvoltage events.
GR-1089-CORE: Electromagnetic Compatibility and Electrical Safety. Published by Telcordia (now part of Ericsson), this standard provides requirements for the electromagnetic compatibility and electrical safety of telecommunications equipment.
FCC Part 68: Connection of Terminal Equipment to the Telephone Network. Outlines the technical requirements for connecting terminal equipment to the public switched telephone network in the United States.
Local building codes and regulations also include requirements for the installation of telecommunication service equipment.
Last update: October 12, 2019
All school districts, colleges, universities and university-affiliated health care systems have significant product, system, firmware and labor resources allocated toward ICT. Risk management departments are attentive to cybersecurity issues. All school districts, colleges, universities and university-affiliated health care systems have significant product, system, firmware and labor resources allocated toward ICT.
The Building Industry Consulting Service International (BICSI) is a professional association supporting the advancement of the ICT community. This community is roughly divided between experts who deal with “outside-plant” systems and “building premise” systems on either side of the ICT demarcation point. BICSI standards cover the wired and wireless spectrum of voice, data, electronic safety & security, project management and audio & video technologies. Its work is divided among several committees:
BICSI Standards Program Technical Subcommittees
BICSI International Standards Program
BICSI has released for public review a new consensus document that supports education industry ICT enterprises: BICSI N1 – Installation Practices for Telecommunications and ICT Cabling and Related Cabling Infrastructure. You may obtain a free electronic copy from: standards@bicsi.org; Jeff Silveira, (813) 903-4712, jsilveira@bicsi.org.
Comments are due November 19th.

You may send comments directly to Jeff (with copy to psa@ansi.org). This commenting opportunity will be referred to IEEE SCC-18 and the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee which meets 4 times monthly in American and European time zones and will meet today. CLICK HERE for login information.

Issue: [18-191]
Category: Telecommunications, Electrical, #SmartCampus
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Michael Hiler
Readings:
What is Grounding and Bonding for Telecommunication Systems?

Adhiyamaan College of Engineering