Alvin Brooks Center for Faith-Justice
- Home Page 69

Mechanical 330
Today’s Handout: Radon, et al (For future dedicated session)
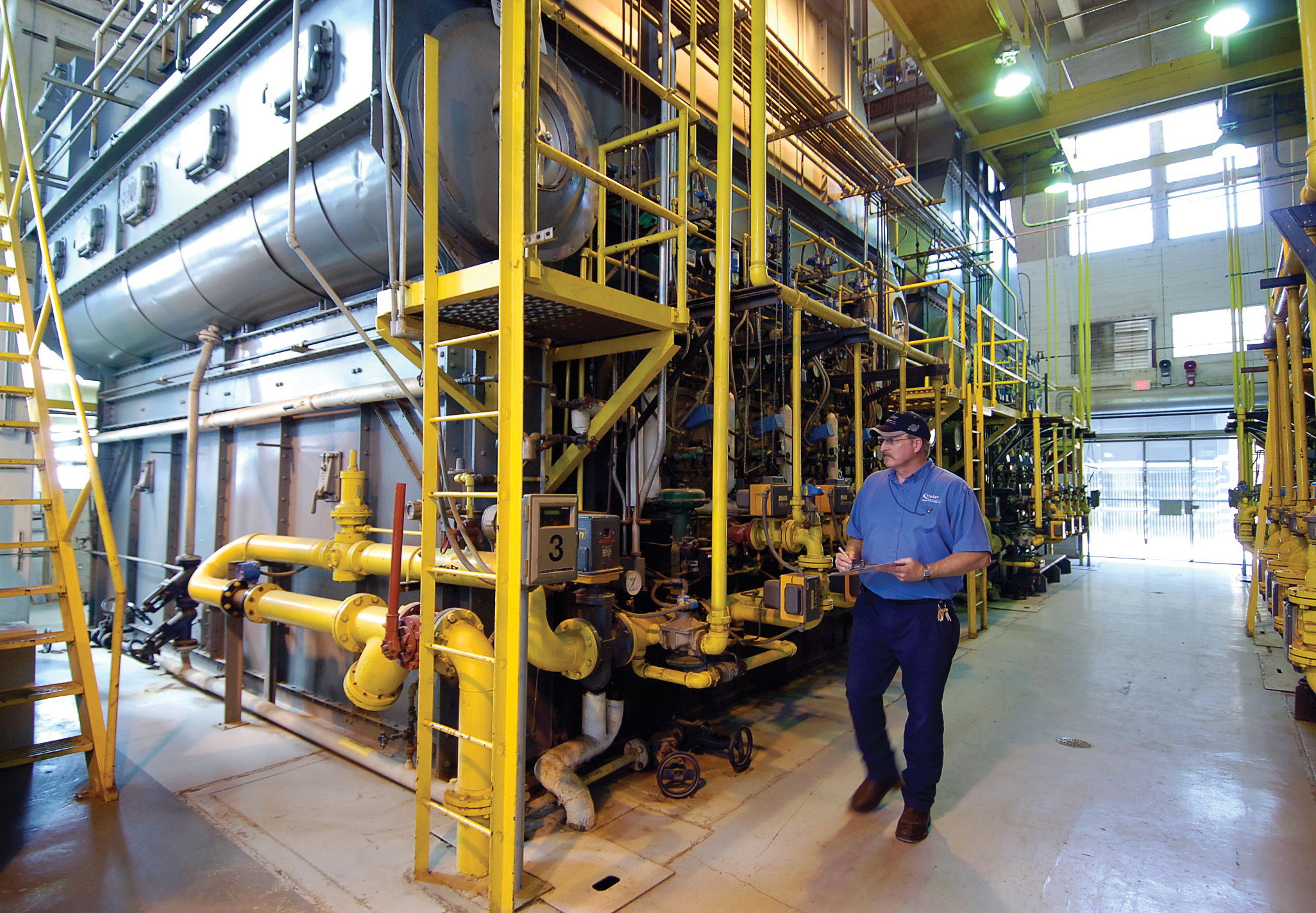
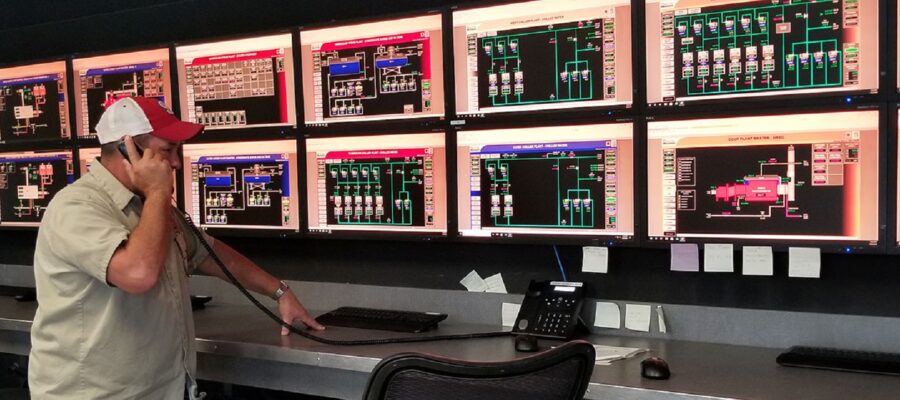
During today’s colloquium we audit the literature that sets the standard of care for mechanical engineering design, construction operations and maintenance of campus district energy systems — typically miles (kilometers) of large underground pipes and wires that characterize a district energy system. Topically, Mechanical 400 deals with energy systems “outside” or “between” buildings; whereas Mechanical 200 deals with energy systems within an individual building envelope.
2024 International Mechanical Code
A campus district energy system is a centralized heating and cooling network that supplies thermal energy to multiple buildings within a defined area, such as a college or university campus. The system generates steam, hot water, or chilled water at a central plant, which is then distributed through an underground network of pipes to individual buildings for space heating, domestic hot water, and air conditioning. By consolidating energy production and distribution, campus district energy systems can achieve significant energy and cost savings compared to individual building systems, as well as reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve reliability and resiliency of the energy supply.






We track standards setting in the bibliographies of the following organizations:
AHRI | Air Conditioning, Heating & Refrigeration Institute
ASHRAE | American Society of Heating & Refrigeration Engineers
ASHRAE Guideline 14: Measurement of Energy and Demand Savings
ASHRAE Guideline 22: Instrumentation for Monitoring Central Chilled Water Plant Efficiency
ASME | American Society of Mechanical Engineers
ASPE | American Association of Plumbing Engineers
ASTM | American Society for Testing & Materials
AWWA | American Water Works Association
AHRI | Air Conditioning, Heating & Refrigeration Institute
IAPMO | International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials
IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission
Institute of Electric and Electronic Engineers
Research on the Implementation Path Analysis of Typical District Energy Internet
Expansion Co-Planning of Integrated Electricity-Heat-Gas Networks in District Energy Systems
Towards a Software Infrastructure for District Energy Management
IMC | International Mechanical Code
IDEA | International District Energy Association
District Energy Best Practices Handbook
District Energy Assessment Tool
IPC | International Plumbing Code
ISEA | International Safety Equipment Association
NFPA | National Fire Protection Association
SMACNA | Sheet Metal Contractors National Association
UL | Underwriters Laboratories
UpTime Institute
(All relevant OSHA Standards)
It is a large domain and virtually none of the organizations listed above deal with district energy systems outside their own (market-making) circle of influence. As best we can we try to pull together the peak priorities for the real asset managers and engineers who are responsible for these system.
* Building services engineers are responsible for the design, installation, operation and monitoring of the technical services in buildings (including mechanical, electrical and public health systems, also known as MEP or HVAC), in order to ensure the safe, comfortable and environmentally friendly operation. Building services engineers work closely with other construction professionals such as architects, structural engineers and quantity surveyors. Building services engineers influence the architectural design of building, in particular facades, in relation to energy efficiency and indoor environment, and can integrate local energy production (e.g. façade-integrated photovoltaics) or community-scale energy facilities (e.g. district heating). Building services engineers therefore play an important role in the design and operation of energy-efficient buildings (including green buildings, passive houses and zero energybuildings. uses. With buildings accounting for about a third of all carbon emissions] and over a half of the global electricity demand, building services engineers play an important role in the move to a low-carbon society, hence mitigate global warming.
More:
Practical Essay on the Stength of Cast Iron and Other Metals Thomas Tredgold (1882)
George Herman Babcock — through his patents of pumps, steam engines, and novel boiler designs with collaborator Stephen Wilcox — raised the standard for safe boiler design & operation.https://t.co/qakAw4jfCn pic.twitter.com/3rCxXHkBfM
— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) October 21, 2020
Installation of Air-Conditioning and Ventilating Systems
Design, construction, operation and maintenance of environmental air, piping and drainage systems is one of the largest cost centers in education facilities. We find subtle tradeoffs between fire safety, energy conservation and indoor air quality goals. With solid data and enlightened debate which include the user-interest (the final fiduciary in the education facility industry, for example) those tradeoffs are reconciled by technical committees administered by three ANSI-accredited standards developers:
American Society of Heating and Refrigeration Engineers (ASHRAE)
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
Sheet Metal & Air Conditioning Contractors National Association
Today we focus on the leading safety practice of NFPA 90A Standard for the Installation of Air-Conditioning and Ventilating Systems. From the NFPA 90A prospectus:
[NFPA 90A] shall cover construction, installation, operation, and maintenance of systems for air conditioning and ventilating, including filters, ducts, and related equipment, to protect life and property from fire, smoke, and gases resulting from fire or from conditions having manifestations similar to fire.
[Explanation A.1.1] An air duct system has the potential to convey smoke, hot gases, and flame from area to area and to supply air to aid combustion in the fire area. For these reasons, fire protection of an air duct system is essential to safety to life and the protection of property. However, an air duct system’s fire integrity also enables it to be used as part of a building’s fire protection system. Guidance for the design of smoke-control systems is provided in NFPA 92, Standard for Smoke Control Systems. Pertinent information on maintenance is provided in Annex B. Maintenance of fire dampers, ceiling dampers, smoke dampers, and combination fire/smoke dampers requirements can be found in NFPA 80, Standard for Fire Doors and Other Opening Protectives, and NFPA 105, Standard for Smoke Door Assemblies and Other Opening Protectives.
The original University of Michigan codes and standards advocacy enterprise spoke loud and clear about duct smoke detector application, control signaling and maintenance requirements from the user point of view. Owing to the re-organization we missed the 2018 revision but we are now recovering from where we left off for the 2021 revision.













The First Draft Report for the 2021 edition is linked below:
First Draft Ballot / Final Results
90A_A2020_AIC_AAA_SD_PCResponses
NFPA 90A is heavily referenced in an interlocking matrix of related fire safety consensus products but it is not very lengthy document. We include it on the standing agenda of our periodic Mechanical and Prometheus Bound teleconference. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
Issue: [13-118]
Category: Fire Protection, Mechanical
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Richard Robben, Larry Spielvogel
:
International Mechanical Code
2024 / 2025 / 2026 Code Development: Group B (2025)
After architectural trades, the mechanical technologies occupy the largest part of building construction:
- HVAC:
- Heating Systems: Technologies include furnaces, boilers, heat pumps, and radiant heating systems.
- Ventilation Systems: Incorporating technologies like air handlers, fans, and ductwork to ensure proper air circulation.
- Air Conditioning Systems: Including central air conditioning units, split systems, and variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems.
- Plumbing:
- Water Supply Systems: Involving technologies for water distribution, pumps, and pressure regulation.
- Sanitary Systems: Including drainage, sewage systems, and waste disposal technologies.
- Fixtures and Faucets: Incorporating technologies for sinks, toilets, showers, and other plumbing fixtures.
- Fire Protection:
- Fire Sprinkler Systems: Employing technologies like sprinkler heads, pipes, pumps, and water tanks.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Including technologies such as gas-based or foam-based suppression systems.
- Energy Efficiency Technologies:
- Energy Management Systems (EMS): Utilizing sensors, controllers, and software to optimize energy consumption in HVAC systems.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Incorporating technologies like heat exchangers to recover and reuse energy from exhaust air.
- Building Automation (BAS):
- Control Systems: Using sensors, actuators, and controllers to manage and automate various mechanical systems for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Smart Building Technologies: Integrating with other building systems for centralized control and monitoring.
- Materials and Construction Techniques:
- Piping Materials: Selecting appropriate materials for pipes and fittings based on the application.
- Prefab and Modular Construction: Leveraging off-site fabrication and assembly for mechanical components.
Our examination of the movement in best practice in the mechanical disciplines usually requires an understanding of first principles that appear in the International Building Code
2024 International Mechanical Code
Current Code Development Cycles (2024-2026)
2024/2025/2026 Code Development Schedule
| “On the Mechanical Equivalent of Heat” | 1850 James Prescott Joule | Proceedings of the Royal Society of London |
Representative Design Guidelines:
US Department of Energy: Sandia National Laboratories
Related:
ICC Releases 2024 International Codes
We are waiting for the link to the Complete Monograph for the Group A cycle in which one of our proposals (Chapter 27 Electrical) will be heard at the April 2023 Committee Action Hearings in Orlando.
Superceded:
Because of the larger, disruptive concepts usually require more than one revision cycle — i.e. 3 to 9 years — it is wise to track those ideas in the transcripts of public hearings on the revisions. For example, the ICC Group A Committee Action Hearings were completed (virtually) in May 2021. The complete monograph of proposals is linked below:
2021 Group A Complete Proposed Changes
Transcript of committee response is linked below:
2021 REPORT OF THE COMMITTEE ACTION HEARINGS ON THE 2021 EDITIONS OF THE GROUP A INTERNATIONAL CODES
A sample of the topics that need attention that involve the mechanical disciplines (e.g. energy, environmental air, water) :
- Soil gas and carbon monoxide detection and mitigation
- Minimum number of required plumbing fixtures in schools and higher education community facilities
- Fixtures for adult changing stations and gender neutral toilet and bathing facilities
- Fat, oil and grease interceptors in kitchens
- Dormitories, residence halls
There are others ideas that can be tracked in the most recent Group B Hearings included April 6th:
Proposals for the 2024 IMC revision will be accepted until January 7, 2024. We maintain this title among our core titles during our periodic Mechanical teleconferences. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.






2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
Issue: [Various]
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Richard Robben, Larry Spielvogel
Group A includes the following codes:
- International Building Code (IBC) – Egress, Fire Safety, General Portions
- International Fire Code (IFC)
- International Fuel Gas Code (IFGC)
- International Mechanical Code (IMC)
- International Plumbing Code (IPC)
- International Private Sewage Disposal Code (IPSDC)
- International Residential Code (IRC) – Mechanical, Plumbing
- International Swimming Pool and Spa Code (ISPSC)
- International Zoning Code (IZC)
- International Property Maintenance Code (IPMC)
- International Wildland-Urban Interface Code (IWUIC)
ICC Code Development Process: Important Links
Apple Picking Robot
AI Institute for Transforming Workforce & Decision Support
👀😍#GoBeavs pic.twitter.com/4pVt0nSXsl
— Oregon State University (@OregonState) February 21, 2023
Charlie Kirk (August 12, 2025): “Has U.S. President Donald Trump gone too far?”
The Oxford Union Society is the world’s most prestigious debating society, with an unparalleled reputation for bringing international guests and speakers to Oxford. Since 1823, the Union has been promoting debate and discussion not just in Oxford University, but across the globe.
My remarks at Oxford Union formal debate.
Has Trump gone too far?
The UK is lost, but it can find its way back if it follows America’s lead. pic.twitter.com/BjajLSRXOK
— Charlie Kirk (@charliekirk11) August 12, 2025
Vedika Rastogi | This House Believes Woke Culture Has Gone Too Far – 1/8 | Oxford Union
Alex Jackson | This House Believes Woke Culture Has Gone Too Far – 2/8 | Oxford Union
Toby Young | This House Believes Woke Culture Has Gone Too Far – 3/8 | Oxford Union
Yasmin Benoit | This House Believes Woke Culture Has Gone Too Far – 4/8 | Oxford Union
Tommy Nguyen | This House Believes Woke Culture Has Gone Too Far – 5/8 | Oxford Union
James Lindsay | This House Believes Woke Culture Has Gone Too Far – 6/8 | Oxford Union
Benjamin Butterworth | This House Believes Woke Culture Has Gone Too Far – 8/8 | Oxford Union
Student Loans
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Dance Wyoming
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Wiener Melange
Zaha Hadid Architects | Standards Austria | International Commission on Illumination
Wiener Melange is a classic Viennese coffee specialty originating in 19th-century. The traditional standard consists of a shot of espresso or strong black coffee (often Mokka) mixed with steamed milk in equal parts, topped with a generous dollop of frothy milk foam. Unlike a cappuccino, it skips cocoa dusting and emphasizes a velvety texture.
Sugar is optional, served on the side. Frequently paired with Apfelstrudel and a glass of water.
Die Universität Wien verabschiedet sich von X/Twitter. 👋
Für Updates aus der Welt der Universität Wien folgt uns auf unseren Social Media-Channels auf Bluesky, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube & Co.! 🏛 👨🔬👩🔬 #univie pic.twitter.com/zSdMF8L1Wt— Universität Wien (@univienna) November 25, 2024
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670




















