Holiday Leftovers
- Home Page 10

2026 National Patent Application Drafting Competition
The NPADC is a team competition for law students to develop skills in drafting patent applications, focusing on U.S. patent law. Teams receive a hypothetical invention statement, conduct prior art searches, draft specifications and claims, and present their work to judges, including patent examiners and practitioners. For 2025, the invention was an extra-uterine system for supporting premature fetuses, indicating the complexity of tasks involved
There is no publicly available timetable for the 2026 National Patent Application Drafting Competition (NPADC) from the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) as of the latest available information. The USPTO typically releases detailed schedules for the NPADC closer to the competition year, often in the fall of the preceding year (e.g., October or November 2025 for the 2026 competition).
After months of hard work, the top five teams met at USPTO headquarters today for the final round of the 2025 National Patent Application Drafting Competition. 🏆 And the winners are … ⬇️
🥇 First place — @UofMNLawSchool pic.twitter.com/uwNSJR0oBy
— USPTO (@uspto) April 4, 2025
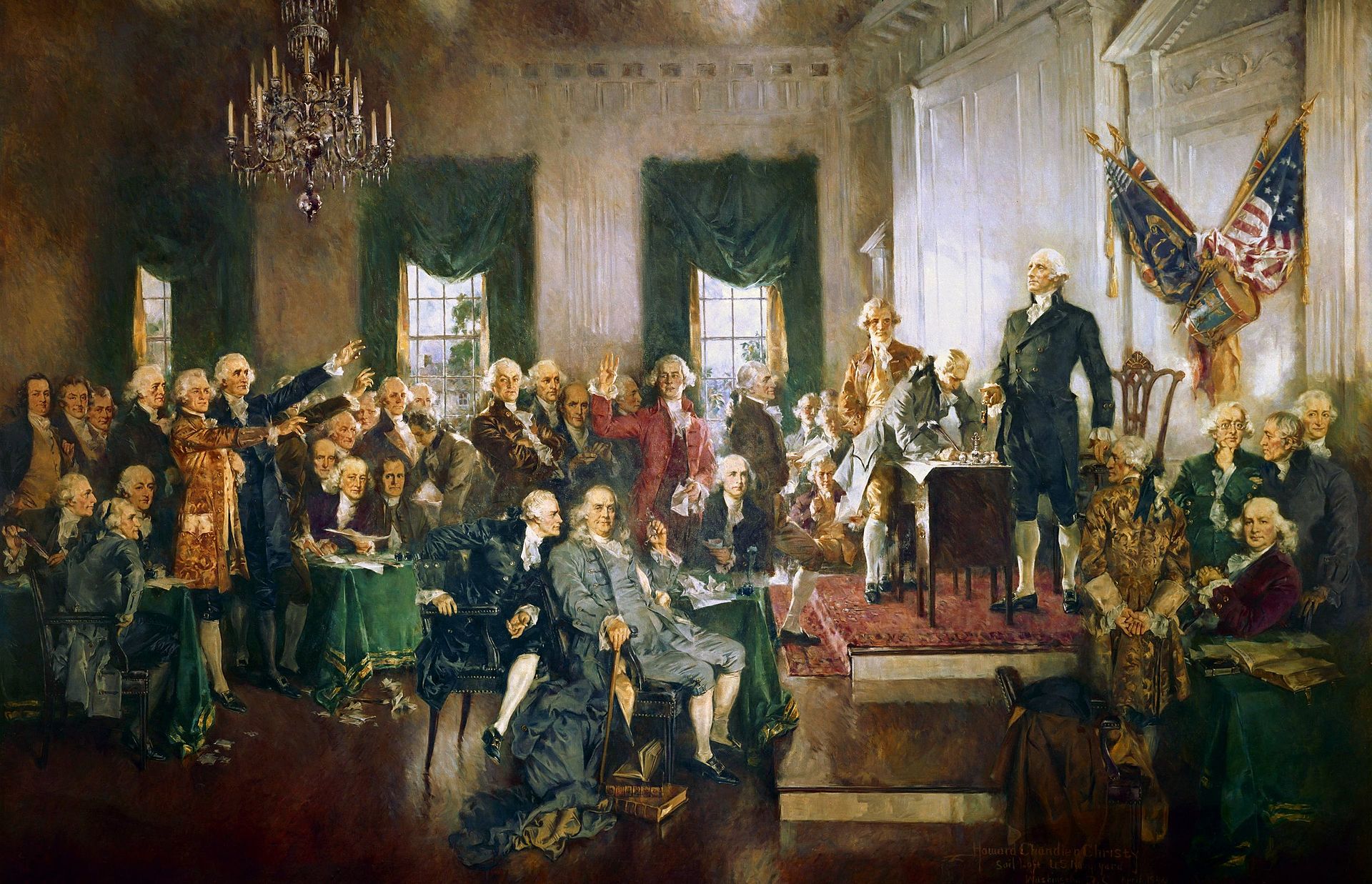
Thomas Jefferson was the leader in founding the United States Patent Office. Jefferson was a strong supporter of the patent system and believed that it was essential for promoting innovation and progress in the United States. As the first Secretary of State Jefferson was responsible for implementing the country’s patent system.
Article I, Section 8, Clause 8 of the United States Constitution reads as follows:
“The Congress shall have Power To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries.”
In 1790, Jefferson drafted the first Patent Act, which established the procedures for applying for and granting patents. The act also created the United States Patent Office as a government agency to oversee the patent system. Jefferson appointed the first Patent Board, which was responsible for reviewing patent applications and making recommendations to the Secretary of State.
Jefferson was deeply involved in the early development of the Patent Office and was instrumental in shaping its policies and procedures. He believed that the patent system should be accessible to all inventors, regardless of their social or economic status, and he worked to streamline the patent application process to make it more efficient and user-friendly.
In recognition of his contributions to the development of the patent system, Jefferson is often referred to as the “Father of American Innovation.”
This clause grants Congress the authority to establish a system of patents and copyrights to protect the intellectual property of inventors and authors. The purpose of this system is to encourage innovation and creativity by providing inventors and authors with a temporary monopoly on their creations, allowing them to profit from their work and invest in future projects. The clause also emphasizes the importance of promoting the progress of science and the useful arts, reflecting the belief of the founders that the development of new technologies and inventions was essential for the growth and prosperity of the United States.
Over the years, the Patent Office has played a crucial role in the development of the United States as a technological leader, granting patents for inventions ranging from the telephone and the light bulb to the airplane and the computer. Today, the Patent Office is part of the United States Department of Commerce and is responsible for examining patent applications and issuing patents to inventors and companies.
Welcome to the 2025 National Patent Application Drafting Competition!
2024 National Patent Application Drafting Competition
Congratulations to the winners of this year’s National Patent Application Drafting Competition – Khailee, Bree, Rita, and Maria from @gwlaw, and thank you to all participants! Learn more about the competition: https://t.co/gB64fnXaM6 pic.twitter.com/FWqak6Mr1m
— USPTO (@uspto) April 14, 2023
From creating a race car safety device that protects drivers from injury to revolutionizing chemotherapy, Spartans have contributed to more than 3,300 inventions. #SpartansWill pic.twitter.com/dchCs0BFBx
— MSU (@michiganstateu) February 21, 2025
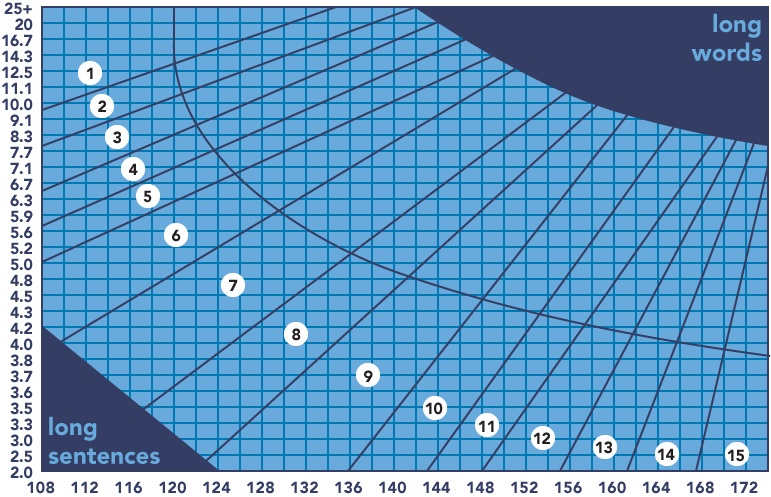
Design Standard Readability
Abstract. Research problem: Readability equations are widely used to compute how well readers will be able to understand written materials. Those equations were usually developed for nontechnical materials, namely, textbooks for elementary, middle, and high schools. This study examines to what extent computerized readability predictions are consistent for highly technical material – selected Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and International Standards Organization (ISO) Recommended Practices and Standards relating to driver interfaces. Literature review: A review of original sources of readability equations revealed a lack of specific criteria in counting various punctuation and text elements, leading to inconsistent readability scores. Few studies on the reliability of readability equations have identified this problem, and even fewer have systematically investigated the extent of the problem and the reasons why it occurs. Research questions:
(1) Do the most commonly used equations give identical readability scores?
(2) How do the scores for each readability equation vary with readability tools?
(3) If there are differences between readability tools, why do they occur?
(4) How does the score vary with the length of passage examined?
Method: Passages of varying lengths from 12 selected SAE and ISO Recommended Practices and Standards were examined using five readability equations (Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level, Gunning Fog Index, SMOG Index, Coleman-Liau Index, and Automated Readability Index) implemented five ways (four online readability tools and Microsoft Word 2013 for Windows). In addition, short test passages of text were used to understand how different readability tools counted text elements, such as words and sentences. Results and conclusions: The mean readability scores of the passages from those 12 SAE and ISO Recommended Practices and Standards ranged from the 10th grade reading level to about 15th. The mean grade reading levels computed across the websites were: Flesch-Kincaid 12.8, Gunning Fog 15.1 SMOG 12.6, Coleman-Liau 13.7, and Automated Readability Index 12.3. Readability score estimates became more consistent as the length of the passage examined increased, with no noteworthy improvements beyond 900 words. Among the five readability tools, scores typically differed by two grade levels, but the scores should have been the same. These differences were due to how compound and hyphenated words, slashes, numbers, abbreviations and acronyms, and URLs were counted, as well other punctuation and text elements. These differences occurred because the sources for these equations often did not specify how to score various punctuation and text elements. Of the tools examined, the authors recommend Microsoft Word 2013 for Windows if the Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level is required.
ICYMI. The OED has recently been updated with:
new words, phrases and senses added
more than 1,000 entries revised
new audio files and pronunciation transcriptions from Northern England and North-Eastern England
and more!Learn more: https://t.co/JCLcZzTtEQ pic.twitter.com/FhdbPKxBVZ
— The OED (@OED) April 4, 2025
Virginia Woolf: pic.twitter.com/8IPw1Fmevk
— Dr. Maya C. Popa (@MayaCPopa) May 25, 2023
Rock of Ages (סלע הגילאים)
Lyrics, Augustus Toplady 1776 | Calvin University Hymnary Kent County Michigan
Today’s weather is ‘snow’ joke! ❄️ pic.twitter.com/JXxwEN6Vll
— Brown University (@BrownUniversity) December 20, 2024
Christ Chapel
“De re aedificatoria” | Leon Battista Alberti
Christianity is surging in America.
We will not become Europe.
— Eric Daugherty (@EricLDaugh) October 25, 2025
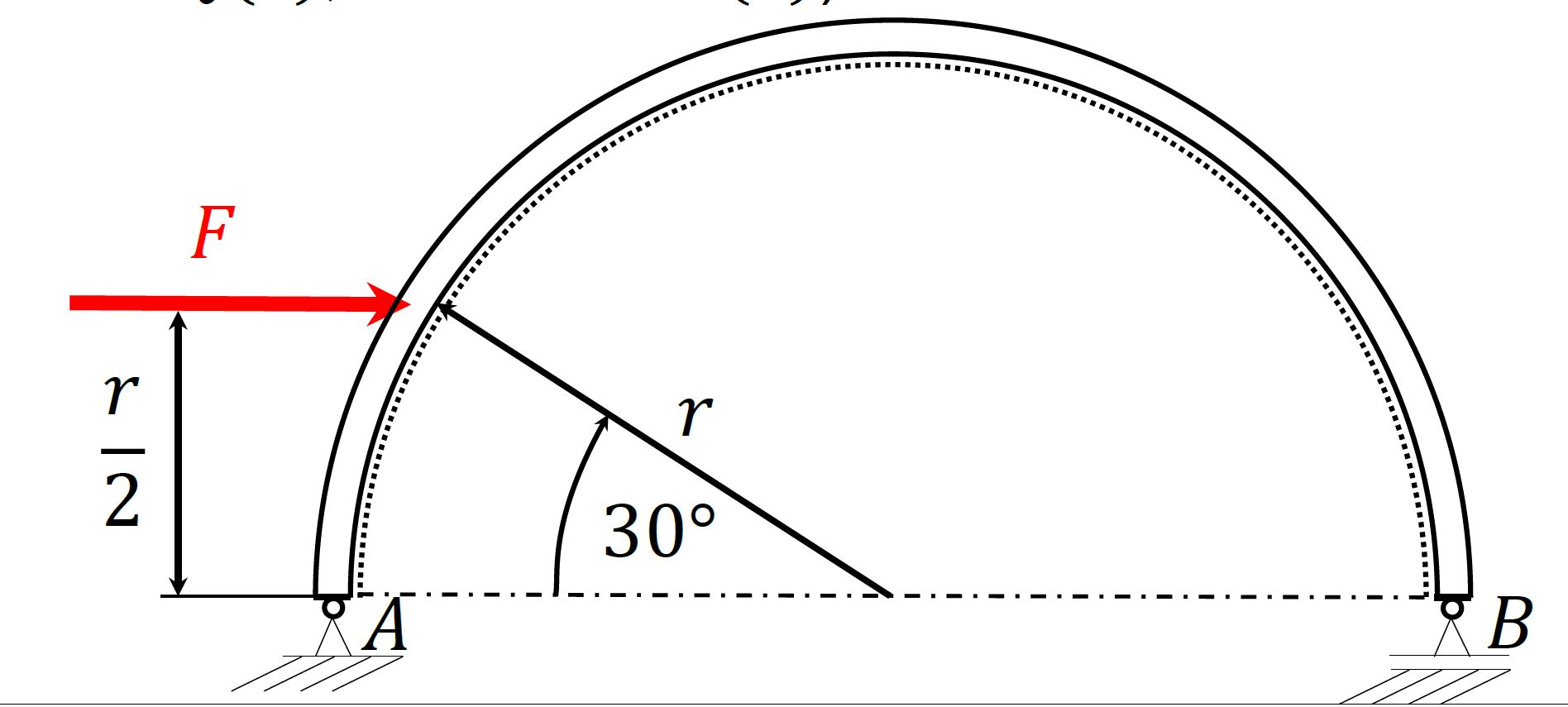
Compute the stress curves for the half-circular arch beam
Gallery: Graduation Commencement Speeches
“It is at leaving the college and entering the world that the education of youth begins…
It is less uniform than that of childhood but more dependent on chance, and doubtless more important.
The youth is then attacked by a greater number of sensations: all that surrounds him strikes him,
and strikes him forcibly.”
— Claude-Adrien Helvétius (A Treatise on Man)
Constructor University (formerly, Jacobs University Bremen Germany) Graduation Band: “Freebird”
Intercollegiate Studies Institute | What Makes the West Strong (Sir Roger Scruton)
Catcher in the Rye
Internet Archive: “Catcher in the Rye” 1951 , J.D. Salinger
Harold Bloom’s Catcher in the Rye Critical Readings
Selected quotes:
“I’m quite illiterate, but I read a lot.”
“It’s funny. All you have to do is say something nobody understands and they’ll do practically anything you want them to.”
“The mark of the immature man is that he wants to die nobly for a cause, while the mark of the mature man is that he wants to live humbly for one.”
“I like it when somebody gets excited about something. It’s nice.”
“If a girl looks swell when she meets you, who gives a damn if she’s late? Nobody.”
Related:
“For Esme, with Love and Squalor” 1950, J.D. Salinger
— Edward Elderman (@edwereddie) November 26, 2025
Mince Pie & Tea
BSI Group: Consumer, Retail & Food Standards
Higher Education (Freedom of Speech) Act 2023
This British festive pastry has origins dating back to the 13th century when European Crusaders returned from the Middle East with recipes containing meats, fruits, and spices. These early pies, known as “mincemeat pies,” combined minced meat (usually mutton), suet, fruits, and spices such as cinnamon, cloves, and nutmeg, symbolizing the gifts of the Magi. In the 16th century, the pies were rectangular, representing Jesus’ crib.
Over time, the meat content reduced, and by the Victorian era, the recipe had evolved to primarily include dried fruits, suet, and spices, aligning with the modern version of the mince pie. Traditionally enjoyed during the Christmas season, mince pies are now small, round pastries filled with a mixture called mincemeat, which typically contains no meat but a blend of dried fruits, sugar, spices, and sometimes brandy or other spirits.
Good luck to all candidates doing their Oxford interviews over the next couple of weeks 🤞
📷 Instagram | Juncao_Oxford#ApplyingToOxford pic.twitter.com/sqj0LpKdgD
— University of Oxford (@UniofOxford) December 9, 2024
Last night, after a 3 year break, we were delighted to once again host our Festive Networking Drinks 🎄 in person, at the Oxford & Cambridge Club, London.
We had a great turn out with almost 60 fellows, students & alumni braving the cold to socialise & network with their peers. pic.twitter.com/WX7aVskMsi— Kellogg College, University of Oxford (@KelloggOx) December 14, 2022
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670