The heating and cooling requirements of K-12 schools, college and university educational, medical research and healthcare delivery campuses are a large market for boiler pressure vessel manufacturers, installers, maintenance personnel and inspectors. The demand for building new, and upgrading existing boilers — either single building boilers, regional boilers or central district energy boilers — presents a large market for professional engineering firms also. A large research university, for example, will have dozens, if not well over 100 boilers that heat and cool square footage in all climates throughout the year. The same boilers provide heating and cooling for data centers, laundry operations, kitchen steam tables in hospitals and dormitories.
The safety rules for these large, complex and frankly, fearsome systems, have been developed by many generations of mechanical engineering professionals in the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC). From the BPVC scope statement:
“…The International Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code establishes rules of safety — relating only to pressure integrity — governing the design, fabrication, and inspection of boilers and pressure vessels, and nuclear power plant components during construction. The objective of the rules is to provide a margin for deterioration in service. Advancements in design and material and the evidence of experience are constantly being added…”
Many state and local governments incorporate the BPVC by reference into public safety regulations and have established boiler safety agencies. Boiler explosions are fairly common, as a simple internet search on the term “school boiler explosion” will reveal. We linked one such incident at the bottom of this page.
The 2023 Edition of the BPVC is the current edition; though the document is divided into many sections that change quickly.
ASME Codes & Standards Electronic Tools
ASME Proposals Available For Public Review
ASME Section IV: Rules for the Construction of Heating Boilers (2019)
Public consultation on changes to the BPVC standard for power boilers closes February 3rd.
This is a fairly stable domain at the moment. We direct you elsewhere to emergent topics:
Ghost kitchens gaining steam on college campuses
College: the Next Big Frontier for Ghost Kitchens
Illinois Admin. Code tit. 77, § 890.1220 – Hot Water Supply and Distribution
Design Considerations for Hot Water Plumbing
FREE ACCESS: 2019 ASME Boiler and Pressure Code (Section VI)
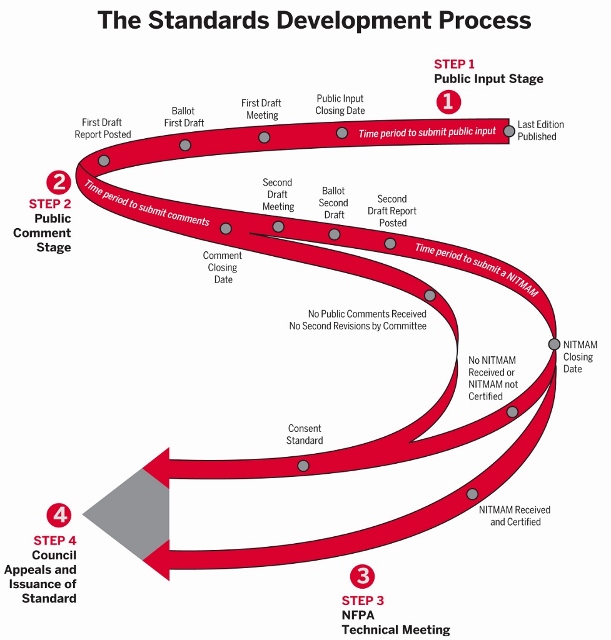
Two characteristics of the ASME standards development process are noteworthy:
- Only the proposed changes to the BPVC are published. The context surrounding a given change may be lost or not seen unless access to previous version is available. Knowledgeable experts who contribute to the development of the BPVC usually have a previous version, however. Newcomers to the process may not.
- The BPVC has several breakout committees; owing to its longer history in the US standards system and the gathering pace of complexity in this technology.
We unpack the ASME bibliography primarily during our Mechanical, Plumbing and Energy colloquia; and also during our coverage of large central laundry and food preparation (Kitchens 100) colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting, open to everyone.
Issue: [12-33] [15-4] [15-161] [16-77] [18-4] [19-157]
Category: District Energy, Energy, Mechanical, Kitchens, Hot Water
Contact: Eric Albert, Richard Robben, Larry Spielvogel
More:
Standards Michigan BPVC Archive
Big Ten & Friends Energy Conference 2023
Standards Michigan Workspace (Requires access credentials from bella@standardsmichigan.com).
School Boiler Maintenance Programs: How Safe Are The Children?
Boiler Explodes at Indiana High School
Engineers at @virginia_tech are boosting heat transfer by prompting bubbles to jump from a heated plate during boiling, potentially increasing power plant efficiency with microstructures: https://t.co/W1gLvhn15q pic.twitter.com/45PNRAEmpB
— ASME.org (@ASMEdotorg) January 30, 2024