Patent No. 558,393 : Flaked cereals and process of preparing same
- Home Page 107

Open Air Audio
Audio Engineering Society Guideline AES56-2008 which provides recommendations for loudspeaker placement in sound reinforcement systems. Key points include:
-
- Height and Angle: Line array speakers are often elevated (e.g., on trusses or poles) and angled to cover the audience while reducing sound spill to non-audience areas.
- Distance: Main speakers should be placed to avoid excessive sound pressure near the front (e.g., 95–100 dBA max for audience safety) and ensure clarity at the back.
Acoustical Society of America ASA-2010 Acoustical Performance Criteria, Design Requirements, and Guidelines for Schools. While primarily for schools, this standard’s principles can apply to open-air educational or community events, emphasizing background noise control and speech intelligibility. For open-air audiences at events like outdoor lectures or festivals, speaker placement should minimize interference from environmental noise (e.g., traffic, wind). The standard suggests maintaining a signal-to-noise ratio where speech is at least 15 dB above background noise for clarity.
Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
Related:
Qualified Zone Academy Bonds
From the Wikipedia:
Qualified Zone Academy Bonds (QZABs) are a U.S. government debt instrument created by Section 226 of the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997. It was later revised and regulations may be found in Section 54(E) of the U.S. Code. QZABs allow certain qualified schools to borrow at nominal interest rates (as low as zero percent) for costs incurred in connection with the establishment of special programs in partnership with the private sector…
…Funds can be used for renovation and rehabilitation projects (including energy projects), as well as equipment purchases (including computers). QZABs cannot be used for new building construction. The school district must obtain matching funds from a private-sector/non-profit partner equal to at least 10% of the cost of the proposed project. Information on the two QZAB federal mandates, 10% match and academy, can be obtained by visiting the American Association of School Administrators (AASA) school financing toolkit (see resources below).
…The normal annual allocation each year has been $400,000,000. However, during 2008, 2009, and 2010, the American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA) increased these amounts to 1.4 billion. The 2011 allocation has returned to the $400,000,000 level. The allocation is divided up by all fifty states and US possessions. QZABs are a temporary program, subject to reauthorization. The last authorization was for the calendar years 2012 and 2013. Authorizations must be used within two years following the year for which they were given, meaning that authorizations given in 2012 must be used by December 31, 2014. As of July 21, 2014, the reauthorization of the QZAB program for years 2014 and 2015 has not been passed by the U.S. Congress. [Emphasis added*]…
From the US Department of Education:
…Schools usually fund large projects, like building renovation or construction, through debt mechanisms such as tax-exempt bonds or loans. School districts must then pay a substantial amount of interest on this debt. For schools serving low income students, QZABs reduce the burden of interest payments by giving financial institutions holding the bonds (or other debt mechanism) a tax credit in lieu of interest. The school district must still pay back the amount of money it initially borrowed, but does not have to pay any interest — typically about half the cost of renovating a school. The credit rate for QZABs sold on a given day is set by the Treasury Department…
With the COVID-19 pandemic disrupting education facility construction projects — and the prospect of at least 10 percent of the built environment rendered redundant for all time — it is enlightening to review the several sources of financing for these construction projects.
We review education industry construction project status and financing at least twice a month during our US Census Bureau Monthly Construction and Finance teleconferences. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone. Use the login credential at the upper right of our home page.
* The Rebuild America’s Schools Act of 2019 (H.R. 865/S. 266)
LEARN MORE:
Ogród na dachu biblioteki
“It is impossible to communicate to people who have not experienced it–
the undefinable menace of total rationalism.” Czesław Miłosz
Polish Committee for Standardization
Rainwater Catchment Systems
One of several titles asserting best practice for rainwater catchment systems — an emergent design feature many college and university facility departments are signaling to demonstrate their conformity to the campus sustainability zietgeist — is ASPE 63 Rainwater Catchment Systems; developed and published by the American Society of Plumbing Engineers. From the project prospectus:
Scope: This standard covers requirements for the design and installation of rainwater catchment systems that utilize the principle of collecting and using precipitation from a rooftop and other hard, impervious building surfaces. This standard does not apply to the collection of rainwater from vehicular parking or other similar surfaces.
Project Need: The purpose of this standard is to assist engineers, designers, plumbers, builders/developers, local government, and end-users in safely implementing a rainwater catchment system.
Stakeholders: Plumbing engineers, designers, plumbers, builders/developers, local government, end users.
You may obtain a copy of the 2020 edition by contacting Gretchen Pienta, (847) 296-0002, gpienta@aspe.org, 6400 Shafer Court, Suite 350, Rosemont, IL 60018. We encourage front-line/workpoint experts and facility managers to participate in the ASPE standards development process. Start with the link below:
ASPE Standards Development Home Page
We have all water system codes and standards on the agenda of our next monthly Mechanical, Plumbing and Rain colloquia See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [13-61]
Category: Mechanical Engineering, Water
Colleagues: Richard Robben, Larry Spielvogel
Related: Posted 10 September 2020
Solar (Summer)
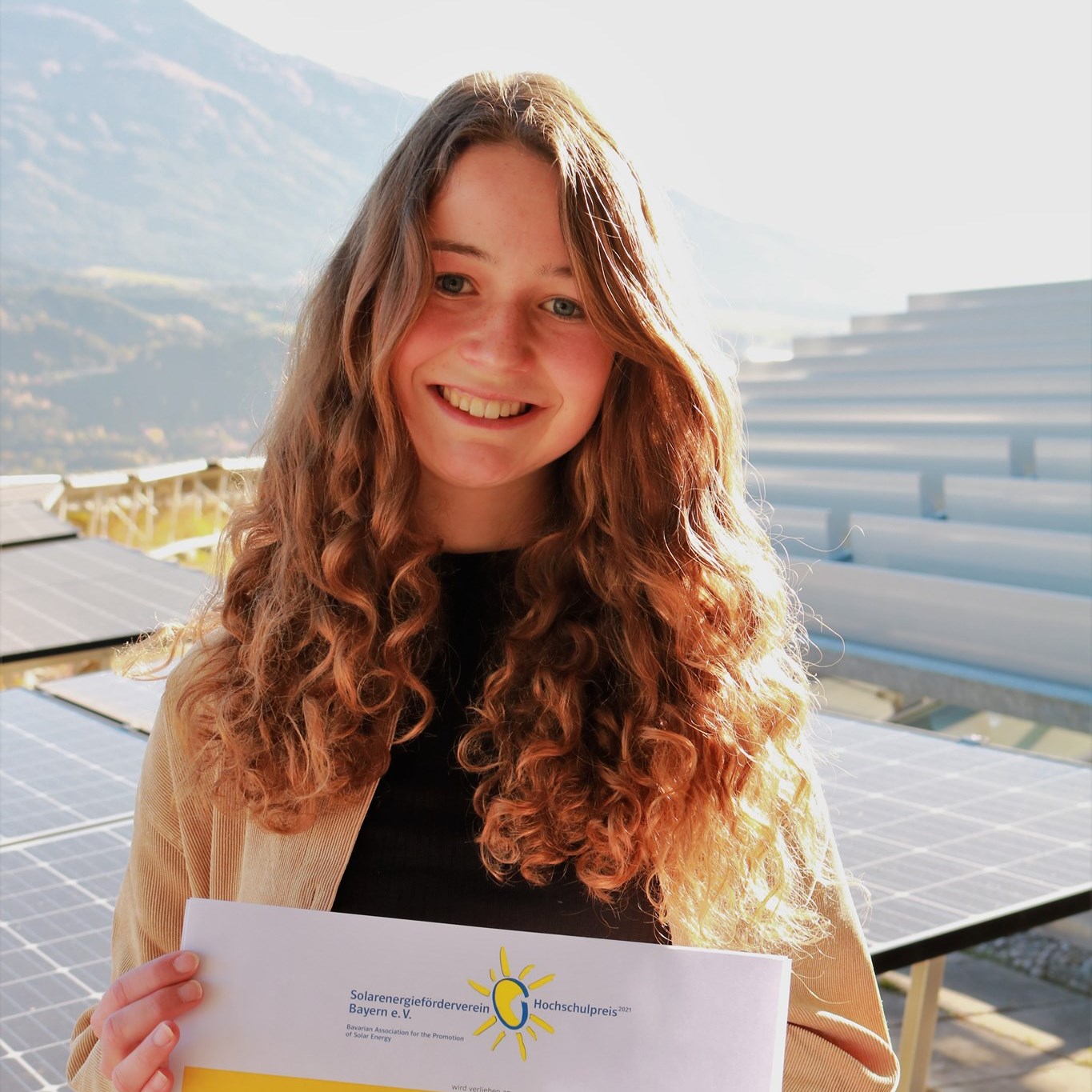
| Sie strahlt vor Freude über ihre Auszeichnung – TH-Alumna Melanie Klaus. Für ihre Bachelorarbeit im Bereich Erneuerbare Energien wurde sie vom Solarenergieförderverein Bayern geehrt. In ihrer Bachelorarbeit im Studiengang Elektro- und Informationstechnik untersuchte sie das Zusammenspiel von Wind- und Solarenergie und den Nutzen, der sich hieraus für die regenerative Energieerzeugung erzielen lässt. Untersucht wurde also die Nutzung der natürlichen Kombination von Wind und Sonne für die Energieerzeugung. Um die Rentabilität dieser Einspeisekombination zu ermitteln, hat Melanie Klaus ein Software-Tool entwickelt, welches zur Planung und Simulation abgestimmter Photovoltaik-Wind-Kombinationen dient und bereits für die Errichtung einer Photovoltaik-Anlage zu einem Windpark eingesetzt wird. |
Starting 2023 we separated our coverage of solar energy standards from our standing Electrical and Energy colloquia and placed emphasis on seasonal life cycle returns. We start with the following titles
IEC TC 82 Solar photovoltaic energy systems
Underwriters Laboratories 1703 PV Module Certification
ASTM E772 Standard Terminology of Solar Energy Conversion
IEEE 1562 Guide for Array and Battery Sizing in Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems
NEMA Solar Photovoltaic Council
NECA 412 Standard for Installing and Maintaining Photovoltaic Power Systems
NFPA 70 Articles 690-691
NFPA 70 Articles 705 & 855
International Code Council Section 1607 Photovoltaic panels or modules
ASHRAE International: 90.1 Building Energy Code & 189.1 Green Energy Code
Time permitting: Example design specification and construction contract.









Other standards developers and publishers are also present in this domain but this list is where we will start given that we only have an hour. Join us today at 16:00 with the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
Readings:
What are the hidden costs of solar panels?
Do We Have Enough Silver, Copper, And Other Materials To Keep Up With The Growth Of Solar?
Mining Raw Materials for Solar Panels: Problems and Solutions
Solar Photovoltaic Energy Systems
Technical Committee 82 of the International Electrotechnical Commission is charged with preparing international standards for the full length of the solar energy power chain The span of the power chain includes the light input, the cell itself, and the fittings and accessories to the end use (utilization) equipment.
Strategic Business Plan of IEC Technical Committee 82
The United States is the Global Secretariat for TC 82 through the US National Committee of the International Electrotechnical Commission (USNA/IEC) administered by the American National Standards Institute(ANSI). Standards Michigan is a long-standing member of ANSI since our “standards journey” began at the University of Michigan in 1993.
The USNA/IEC and participates in its standards development processes; typically collaborating with global research and application engineers in the IEEE Industrial Applications Society and the IEEE Power and Energy Society. To advance its agenda for lower #TotalCostofOwnership for US real asset executives and facility managers Standards Michigan also collaborates closely with subject matter experts who contribute to, and draw from, the knowledge base in the IEEE Education and Healthcare Facilities Committee (E&H).
The IEC permits public commenting on its draft standards; though you will need to establish login credentials:
Your comments will be reviewed by the IEC National Committee of the country you live in, which can decide to propose them as national input for the final draft of the IEC International Standard. This approach makes it easier for individual nations to participate in IEC standards development processes because the resources that national standards bodies need to administer participation resides in Geneva and is managed there.
We collaborate with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee which has its own platform to tracking commenting opportunities:
As of this posting, no interoperability redlines have been released for public consultation. In large measure, IEC titles contribute to a level playing field among multi-national electrical equipment manufacturers so we should not be surprised that there are no redlines to review. When they are released we place them on the agenda of the IEEE E&H Committee which meets 4 times monthly in European and American time zones.
Log in to the E&H Committee meeting
Issue: [18-240]
Category: Electrical Power, Energy Conservation
Contact: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Peter Sutherland
LEARN MORE:
[1] US Commenters must route their comments through the USNA/IEC.
[2] Many product and installation standards are developed by the Association of Electrical Equipment and Medical Imaging Manufacturers (NEMA): CLICK HERE
[3] NEMA comparison of NEC and IEC electrical safety standards
Solarvoltaic PV Systems
National Electrical Code Articles 690 and 691 provide electrical installation requirements for Owner solarvoltaic PV systems that fall under local electrical safety regulations. Access to the 2023 Edition is linked below;
2026 National Electrical Code Second Draft Transcript | CMP-4
Insight into the technical problems managed in the 2023 edition can be seen in the developmental transcripts linked below:
Panel 4 Public Input Report (869 pages)
Panel 4 Second Draft Comment Report (199 pages)
The IEEE Joint IAS/PES (Industrial Applications Society & Power and Energy Society) has one vote on this 21-member committee; the only pure “User-Interest” we describe in our ABOUT. All other voting representatives on this committee represent market incumbents or are proxies for market incumbents; also described in our ABOUT.
The 2026 National Electrical Code has entered its revision cycle. Public input is due September 7th.
We maintain these articles, and all other articles related to “renewable” energy, on the standing agenda of our Power and Solar colloquia which anyone may join with the login credentials at the upper right of our home page. We work close coupled with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee which meets 4 times monthly in American and European time zones; also open to everyone.
How the Netherlands Prevents Flood Disasters
Federal Flood Risk Management Standard
Floods bring substantial debris along and this exacerbates the flooding. Daan Poppema and his students replicate this in our new outdoor campus flume, measuring the rise when debris blocks the bridge.
💡The future results can enhance our preparedness for future flood events. pic.twitter.com/k5vWvRqBvp
— TU Delft (@tudelft) August 11, 2023
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670