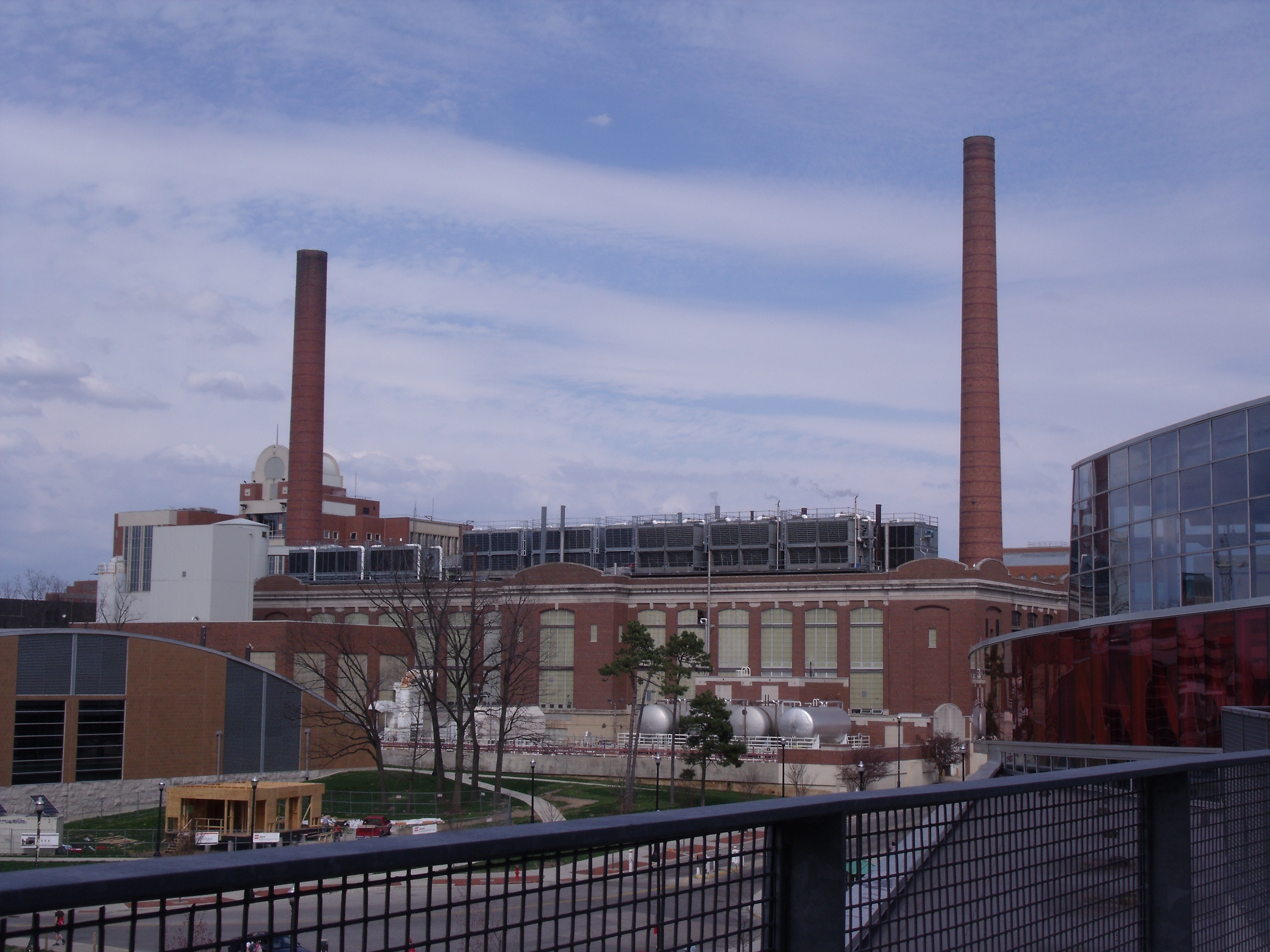
Should every campus building generate its own power? Sustainability workgroups are vulnerable to speculative hype about net-zero buildings and microgrids. We remind sustainability trendsniffers that the central feature of a distributed energy resource–the eyesore known as the university steam plant–delivers most of the economic benefit of a microgrid. [Comments on Second Draft due April 29th] #StandardsMassachusetts
“M. van Marum. Tweede vervolg der proefneemingen gedaan met Teyler’s electrizeer-machine, 1795” | An early energy storage device | Massachusetts Institute of Technology Libraries
We have been following the developmental trajectory of a new NFPA regulatory product — NFPA 855 Standard for the Installation of Stationary Energy Storage Systems — a document with ambitions to formalize the fire safety landscape of the central feature of campus microgrids by setting criteria for minimizing the hazards associated with energy storage systems.
The fire safety of electric vehicles and the companion storage units for solar and wind power systems has been elevated in recent years with incidents with high public visibility. The education industry needs to contribute ideas and data to what we call the emergent #SmartCampus;an electrotechnical transformation — both as a provider of new knowledge and as a user of the new knowledge.
Transcripts of technical deliberation are linked below:
2026 Public Input Report (705 pages) § 2026 Second Draft Meeting Agenda (912 pages)
Comment on the 2026 revision received by March 27, 2025 will be heard at the NFPA June 2025 Expo through NFPA’s NITMAM process.

University of Michigan | Average daily electrical load across all Ann Arbor campuses is on the order of 100 megawatts
A fair question to ask: “How is NFPA 855 going to establish the standard of care any better than the standard of care discovered and promulgated in the NFPA 70-series and the often-paired documents NFPA 110 and NFPA 111?” (As you read the transcript of the proceedings you can see the committee tip-toeing around prospective overlaps and conflicts; never a first choice).
Suffice to say, the NFPA Standards Council has due process requirements for new committee projects and, obviously, that criteria has been met. Market demand presents an opportunity to assemble a new committee with fresh, with new voices funded by a fresh set of stakeholders who, because they are more accustomed to advocacy in open-source and consortia standards development platforms, might have not been involved in the more rigorous standards development processes of ANSI accredited standards developing organizations — specifically the NFPA, whose members are usually found at the top of organization charts in state and local jurisdictions. For example we find UBER — the ride sharing company — on the technical committee. We find another voice from Tesla Motors. These companies are centered in an industry that does not have the tradition of leading practice discovery and promulgation that the building industry has had for the better part of two hundred years.
Our interest in this standard lies on both sides of the education industry — i.e. the academic research side and the business side. For all practical purposes, the most credible, multi-dimensional and effective voice for lowering #TotalCostofOwnership for the emergent smart campus is found in the tenure of Standards Michigan and its collaboration with IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee (E&H). You may join us sorting through the technical, economic and legal particulars and day at 11 AM Eastern time. The IEEE E&H Committee meets online every other Tuesday in European and American time zones; the next meeting on March 26th. All meetings are open to the public.
You are encouraged to communicate directly with Brian O’Connor, the NFPA Staff Liaison for specific questions. We have some of the answers but Brian is likely to have all of them. CLICK HERE for the NFPA Directory. Additionally, NFPA will be hosting its Annual Conference & Expo, June 17-20 in San Antonio, Texas; usually an auspicious time for meeting NFPA staff working on this, and other projects.
The prospect of installing of energy storage technologies at every campus building — or groups of buildings, or in regions — is clearly transformational if the education facilities industry somehow manages to find a way to drive the cost of operating and maintaining many energy storage technologies lower than the cost of operating and maintaining a single campus distributed energy resource. The education facility industry will have to train a new cadre of microgrid technology specialists who must be comfortable working at ampere and voltage ranges on both sides of the decimal point that separates power engineers from control engineers. And, of course, dynamic utility pricing (set by state regulatory agencies) will continue to be the most significant independent control variable.
Finding a way to make all this hang together is the legitimate work of the academic research side of the university. We find that sustainability workgroups (and elected governing bodies) in the education industry are vulnerable to out-sized claims about microgrids and distributed energy resources; both trendy terms of art for the electrotechnical transformation we call the emergent #SmartCampus.
We remind sustainability trendsniffers that the central feature of a distributed energy resource — the eyesore known as the university steam plant — bears most of the characteristics of a microgrid. In the videoclip linked below a respected voice from Ohio State University provides enlightenment on this point; even as he contributes to the discovery stream with a study unit.
Issue: [16-131]
Category: District Energy, Electrical, Energy, Facility Asset Management, Fire Safety, Risk Management, #SmartCampus, US Department of Energy
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Bill Cantor (wcantor@ieee.org). Mahesh Illindala
Standards Massachusetts, Standards Texas, Standards Ohio
*It is noteworthy that (NFPA 70) National Electrical Code-Making Panel 1 has appropriated vehicle-to-grid installations into its scope.
LEARN MORE:
Related Post: Electrical Safety Research Advisory Committee
Bibiography: Campus Microgrids
Higher Education Facilities Conference: The Rise of University Microgrids
Here's an interesting shift – #utilities are starting to invest in big #batteries rather than building new #power plants. Find out why over at @GreenBiz: https://t.co/m0DYK9qAae #energy #EnergyStorage
— IEEE Power & Energy Society (@ieee_pes) February 28, 2019
Mahesh Illindala enlightens understanding of what microgrid is, and is not:
Check out our top story from February 2018 – Making the right battery storage choice for solar panel installations https://t.co/1xyTnd17TF pic.twitter.com/sXJNX0kSfr
— IEC (@IECStandards) January 2, 2019